There are minimum standards set by law for the condition of your vehicle. You must know these standards and make sure your vehicle complies with the law. This section sets out the basic information you need to know.
As a driver, you must make sure that your vehicle is in good working order. You must ensure that the steering, brakes, front and rear lamps, indicators, reflectors, rear view mirrors, safety belts, speedometer, tyres, windscreen wipers, horn and silencer are checked regularly.
If you are the owner of an electric vehicle, ensure that you are familiar with the charging procedure for your vehicle and also the safe operation of charging points.
As an owner of a commercial vehicle, you must put in place a system for the regular inspection and on-going maintenance of your vehicle and ensure it has a valid Certificate of Roadworthiness. This involves implementing the following measures:
- Deciding how often a vehicle is to be inspected, taking into account the age, mileage and condition of the vehicle;
- Ensuring a daily walk-around check of the vehicle is performed before it is driven in a public place, which involves the inspection of both the inside and outside of the vehicle as well as examination of various items such as the mirrors, seatbelts, tyres, exhaust, and so on;
- Keeping records of all inspections, maintenance and repairs of the vehicle
The RSA advises motorists that it would be useful to have the following items available for use in your vehicle:
- A first aid kit,
- At least 1 high-viz vest or jacket (fluorescent and reflective),
- At least 1 red warning triangle (this is required for HGVs and buses),
- A torch, and
- A small fire extinguisher
The items listed above might be useful in an emergency. You might choose to carry other items that you feel might be helpful.
Remember: It is an offence to drive an unsafe vehicle on a public road.
Motor vehicles must be tested for their roadworthiness. This section sets out the minimum standards that your vehicle must meet. You should check the following on a regular basis:
Tyres
Tread depth: Do not allow your tyres to wear down too much. Most vehicles must have a minimum tread depth of 1.6 mm over the main tread, however it is strongly recommended that you consider changing the tyres when they have reached 3 mm.
Pressure: Regularly check the pressure of every tyre, including the spare tyre, and pay attention to the recommended pressure levels. See the manufacturer’s specifications for correct inflation pressure.
Checking for damage: Regularly examine your tyres for cuts, cracks and bulges, which could cause unexpected ‘blow-outs.’
Before you get a flat tyre: Check your vehicle and make sure you know how to change a wheel, that you have a spare wheel and repair kit to hand.
Replacing tyres: For your safety, only fit new and e-marked tyres bought from a reputable dealer. Do not mix radial and cross ply tyres on any one axle. Tyres must be the same on any axle.
Temporary use (space saver) spare tyre or repair kit: Only use these tyres to complete a journey or make a journey to a tyre dealer. Do not travel at a speed in excess of the recommended speed stamped on the tyre.
Remember: Use of secondhand tyres can be risky and should be avoided because there is no history of how they have been used or abused.
Lights and reflectors
Motor vehicles (except motorcycles or electric vehicles with a maximum speed of 38km/h) must have the following lights and reflectors:

At the front:
- Two headlights (white or yellow)
- Two white sidelights
- Direction indicator lights (amber only)
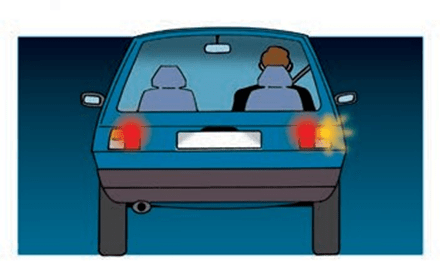
At the back:
- Two red lights (commonly known as tail lights)
- Two red brake lights
- Two red reflectors
- Number plate lighting
- Direction indicator lights (amber only)
Remember: Your lights, reflectors, number plate lighting and direction indicators will be effective only if you keep them clean and in good working order.
Remember:
- You must only use fog lights in dense fog or falling snow. Turn them off in clear weather or you will risk causing glare and may dazzle other drivers.
- You may fit high mounted rear brake lights if you wish, but fitting other optional lighting is controlled by law.
Before you change or alter the physical appearance of your vehicle, for example by fitting spot lights, bull bars or ornaments, take care not to increase the risk to road users, in particular the more vulnerable ones, for example cyclists and pedestrians.
The use of flashing lights, with the exception of direction indicators, is solely reserved for Gardaí, ambulance and other designated service vehicles. You must not fit blue or red flashing lights to your vehicle.
A vehicle must have white or yellow lights showing to the front and red lights showing to the rear, together with amber direction indicators and white or yellow reverse lamps.
You should not make any technical modifications to your vehicle without professional advice as these may have legal and safety implications.
You should also inform your insurance company, as some modifications can invalidate your insurance policy.
It is recommended that dipped headlights only be used when driving or when stopped in traffic. Avoid having them switched on when stopped at the side of the road. You should not use headlights when parked. If you need lights when parked or stopped, use ‘side’ lights or ‘parking’ lights.
If your vehicle is fitted with day time running lights, remember to switch on your dipped head lights at lighting up time.
Remember: Please note that specific reflective markings must be displayed on HGVs and their trailers.
Windscreens
Type of windscreen: Laminated glass must be used for the windscreens of motor vehicles registered since January 1986. It must also be used when replacing damaged windscreens of older vehicles.
Windscreen wipers: Keep your windscreen wipers and wiper blades in good working condition and keep your windscreen washer liquid topped up.
Clear vision: Keep your windscreen and windows clean and free of clutter to make sure you can see the road and other road users clearly.
Mirrors
Your vehicle must have mirrors or approved MirrorCam – side-mounted digital rear-view mirrors – so that you always know what is behind (rear-view) and to each side (door or wing mirrors/cameras).
On large vehicles the fitment of a front mirror, known as a Cyclops mirror, has the potential to reduce fatalities and serious injuries from collisions between HGVs and cyclists or pedestrians.
All HGVs must have Cyclops, close proximity and wide-angle mirrors to eliminate ‘blind spots’ and protect pedestrians and cyclists to the front and sides of the vehicles. This requirement also applies to buses where they have been fitted by the original manufacturer as part of the vehicles type approval process.
Note:
HGVs registered after 2007 are obliged to have these safety-enhancing mirrors.
From 1 October 2012, the HGV annual roadworthiness test includes a check to see that you comply with the regulations.
When to use mirrors: You must use your vehicle’s mirrors before signalling, before moving off, changing lanes, overtaking, slowing down, stopping, turning, or opening doors.
In addition, you should check your mirrors regularly while driving to see what is going on behind your vehicle.
Clear vision: As with lights and reflectors, you must keep your mirrors clean, in good condition and correctly positioned to make sure they are effective.

Safety belts
Where safety belts are fitted, you must wear them. The only exceptions are for:
- People who wear a disabled person’s belt,
- People whose doctors have certified that, on medical grounds, they should not wear a safety belt,
- Driving instructors or driver testers during a lesson or a test, and
- Gardaí or members of the Defence Forces in the course of their duty.
Private buses and heavy goods vehicles registered since 20 October 2007 must have seat belts fitted.
Bus owners are required to present documentation at their bus roadworthiness test certifying that any seat belts fitted to their vehicle meet a minimum safety standard.
Since October 2011, all buses involved in the organised transport of children must be fitted with certified seat belt installations. This requirement does not apply to the transport of children on bus services offered to the general public (scheduled urban or inter-urban bus services).
Child restraint systems
Safety belts are designed mainly for adults and older children. Child safety laws make it compulsory for all children to use the correct child restraint child seat, booster seat or booster cushion. Children under 150 centimetres tall and less than 36 kilograms in weight must be restrained in an appropriate child restraint system when travelling in a passenger car or goods vehicle.
Examples of appropriate restraint systems are baby car seats and booster seats. You must comply with the following:
- Children under 3 years of age must not travel in a car or goods vehicle (other than a taxi) unless restrained in the correct child seat.
- Children aged 3 years or over who are under 150cms in height and weigh less than 36 kilograms (generally children up to 11 or 12 years old) must use the correct child seat or booster cushion when travelling in cars or goods vehicles.
- A rearward-facing child car seat must not be used in the front passenger seat of cars with active airbags.
- A child car seat must be in accordance with EU or United Nations – Economic Commission for Europe (UN-ECE) standards.
- Where safety belts have been fitted, they must be worn.
- Make sure passengers aged under 17 use the correct seat, booster seat, booster cushion or seatbelt. All drivers are legally responsible for this.
You will be breaking the law if you fail to comply with the rules above explaining child restraint system requirements. Specifically, it is an offence for a driver to:
- Allow a passenger under 17 years of age to occupy a seat without wearing a seatbelt,
- Allow a child under 3 years of age to travel in a vehicle without being restrained by an appropriate child restraint,
- Allow a child over 3 years of age to travel in a vehicle without being restrained by an appropriate child restraint, or
- Allow a child to be restrained by a rearward-facing child restraint fitted to a seat which is protected by an active frontal airbag.
Ensuring a child is properly restrained in a child car seat can reduce injuries by up to 90-95% for rear-facing seats and 60% for forward-facing seats*.
What to remember when using child restraints
- Choose a child restraint appropriate to your child’s height and weight. Use the child restraint for every journey, no matter how short.
- Choose a seat that:
- bears an E mark (meaning that it meets United Nations Standard ECE Regulation 44.03, 44.04 or Regulation 129),
- suits the child’s weight and height, and
- is suitable for the type of car it’s being used in.
- There are so many advantages to buying a child car seat brand new, including knowing its history and being confident that there is no damage or missing parts.
- Fit the child seat correctly, according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and seek advice from an expert if you’re unsure.
- It is safer to fit the seat in the back seat of your car.
It is recommended that you buy a child car seat only from a retailer who will check that it fits. Make sure it suits your child and can be fitted safely in your car.
It is also recommended that you have the fitting of your child car seat checked regularly.
Restraints for passengers under 17
By law, the driver of a passenger car or goods vehicle must ensure passengers under 17 years of age wear a safety belt or an appropriate child restraint. You may receive up to 5 penalty points if your passengers in this age group are not belted or restrained.
Roof racks and roof boxes
If you use a roof rack or roof box, you must:
- Securely fit it to your vehicle
- Make sure that the load does not block your view of the road in any direction
- Never overload it
- Never place the load in a way that might cause it to fall off, and
- Never load the rack or box in a way that would destabilise your vehicle.
To be safe, you are strongly advised to check that the roof rack or box is correctly mounted and the load is completely secured before you set off. These checks also apply if you are using a rear or roof-mounted bicycle rack.
Vehicle registration plates
The law sets down what vehicle registration plates must look like. The two diagrams below show the only formats that are allowed for vehicles registered in Ireland on or after 1 January 1991.


Vehicle registration plates must be kept clean and legible. All numbers and letters must be in plain black text on a plain white reflective background. There should be no italics or shadows. You must not interfere with a registration plate.
Other safety responsibilities
As a driver, you have a number of other responsibilities to your passengers.
Children in motor vehicles
You must not leave infants or young children on their own in a motor vehicle, even if you are only away for a short time. The children may face a number of hazards, such as:
- A fire breaking out
- Difficulty in breathing on a warm day (if all windows are closed), and
- Being trapped in electric windows, which could result in serious injury or death.
Animals in motor vehicles
Animals should be securely contained when traveling in a vehicle using an appropriate harness or cage to avoid injury to the animal or to other passengers.
You should never leave animals alone in vehicles. It is cruel and unsafe and can result in injury to the animal and damage to your vehicle.
Using a mobile phone
You must not drive a vehicle or ride a motorbike while using a hand-held mobile phone. It is an offence, for which you may receive a fixed charge and up to 5 penalty points.
You must not send a text message or email or read a text message or email from a mobile phone while driving a vehicle or riding a motorbike. It is an offence for which a person will face a compulsory court appearance and a fine to be determined by the judge. There is also the possibility of a prison term of up to 3 months to be imposed in cases of multiple offences in a 12-month period.
There is no option to take the lesser penalty of penalty points for this offence.
You may only use your mobile phone when you are driving if you are phoning 999 or 112, or you are responding to another type of genuine emergency.
Cyclists should never use a mobile phone when cycling and pedestrians should be careful when using one.
Personal entertainment systems
As a road user, you should avoid using personal entertainment systems through earphones. These systems – for example, personal radios and MP3 players – can distract you, and may prove dangerous when driving or crossing the road. Cyclists in particular should avoid these systems, as they rely on their hearing while on the road.
If you do use a personal or in-car system, play it at a volume that does not distract or prevent you from hearing emergency sirens or car horns.